
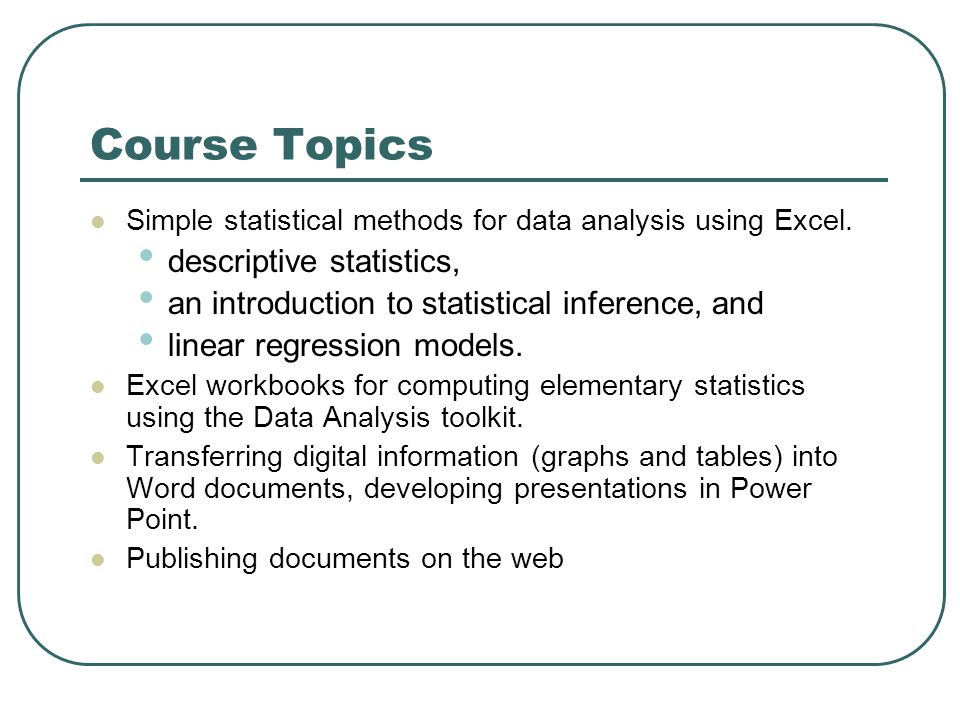
This course combines lecture videos, computer demonstrations, readings, exercises, and discussion boards to create an active learning experience. In particular, the Bayesian approach allows for better accounting of uncertainty, results that have more intuitive and interpretable meaning, and more explicit statements of assumptions. We will compare the Bayesian approach to the more commonly-taught Frequentist approach, and see some of the benefits of the Bayesian approach.
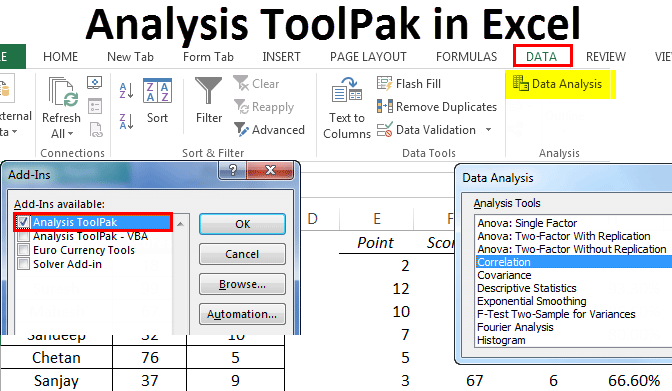
#Basic statistical analysis in excel how to#
We will learn about the philosophy of the Bayesian approach as well as how to implement it for common types of data. The difference is that ratio data has an absolute zero value, and so it makes sense to say, for example, that one data element is 50% bigger than another or twice as effective as another.Ī random variable can be considered metric or non-metric, nominal (or categorical), ordinal, interval or ratio, depending on whether the underlying data corresponding to the random variable has this type.This course introduces the Bayesian approach to statistics, starting with the concept of probability and moving to the analysis of data. There are two types of metric data: interval and ratio data.
As we will see, unlike non-metric data, it makes sense to take the mean, standard deviation, etc.
they can be added, subtracted, multiplied, divided, etc.). Metric data can be manipulated mathematically (i.e. Nominal and ordinal data are called non-metric data. Ordinal data can be compared (thus we can say one data element is greater than another), but they cannot be added or subtracted or calculated in any other way.

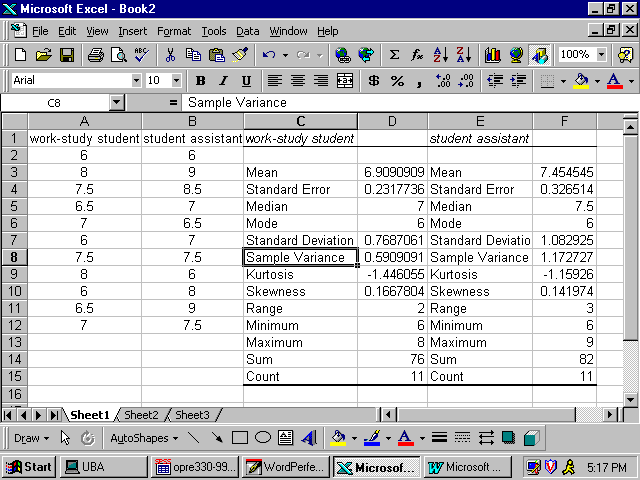
we can’t say Female < Male or Male < Female. Nominal data (also called categorical data) can be labeled, but not calculated or compared. parameter) about the population from which the sample is drawn.ĭata scales: We consider four types of data measurements (i.e. Statistic: a quantity that is calculated from a sample and is used to estimate a corresponding characteristic (i.e. A continuous variable can take an infinite set of values. Discrete variables can take either a finite or infinite set of values, although for our purposes we usually consider discrete variables which only take a finite set of values.Ĭontinuous variable: a variable that can take all the values in a finite or infinite interval (e.g. cards in a deck or scores on an IQ test). Independent random variable: a variable that is chosen, and then measured or manipulated, by the researcher in order to study some observed behavior.ĭependent random variable: a variable whose value depends on the value of one or more independent variables.ĭiscrete variable: a variable which can take a discrete set of values (e.g. We will use letters at the end of the alphabet, especially x, y and z, as random variables. Random variable: a variable that represents value(s) from a random sample. Random sample: a sample in which each member of the population has an equal chance of being included and in which the selection of one member is independent from the selection of all other members. A major objective in the field of statistics is to make inferences about a population based on properties of the sample. Sample: a subset of the data from the population which we analyze in order to learn about the population. A key focus of the field of statistics is the study of characteristics of interest about a population. Population: a complete set of data which we wish to study or analyze. These definitions will be further elaborated throughout the rest of the website.ĭata and data sets: observations from the environment. Theories about a general population are tested on a smaller sample and conclusions are made about how well properties of the sample extend to the population at large.
Statistics is a discipline that is concerned with the collection and analysis of data based on a probabilistic approach. Statistics also plays a central role in decision making for business and government, including marketing, strategic planning, manufacturing and finance. You iterate this process, observing more about the world and improving your theory.Such experiments include collecting data, analyzing the results and coming to some conclusions about how well your theory holds up You then test your theory by conducting experiments.You make some observations about the world and then create a theory consisting of a hypothesis and possible alternative hypotheses that try to explain the observations you have made.A simplified view of experimental research is as follows: Statistics plays a central role in research in the social sciences, pure sciences and medicine.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
